Ever felt like your small business is just wading through quicksand when it comes to technology? Maybe you’re stuck with slow servers, unreliable backups, or that constant, sinking feeling that you’re spending too much just to keep the lights on. If any of that sounds familiar, trust me, you’re in good company.
Here’s the thing we all know: The business world moves at lightning speed. These days, with the massive push toward digital transformation and the new reality of remote work, relying on old, physical hardware is like trying to win a marathon wearing lead shoes. It’s draining, expensive, and it absolutely leaves you behind.
That’s where cloud computing for small business steps in. It’s a totally practical, budget-friendly, and truly essential strategy. It gives small companies – yours included – the power to compete head-to-head with those big players.
This guide is your complete roadmap. We’re going to break down how cloud computing actually works and spell out the major benefits of cloud computing for small businesses. More importantly, we’ll show you exactly how to start using this game-changing technology today. We’ll cover everything, right from how your daily files live in the cloud to the different models that make it all run. By the end, you’ll have a clear, secure, and affordable plan for small business cloud adoption. Let’s get started.
Understanding cloud computing: Basics for small business owners
Cloud computing is really a simple, logical idea. It just means you’re using services over the internet for things like storage, software, and computing power. You do this instead of relying on a big, hot, expensive server box sitting in your office closet.
You skip buying and maintaining your own hardware. Instead, a provider (think Amazon, Microsoft, or Google) hosts all that equipment in their huge, hyper-secure data centers. Then, you just access those powerful resources through a simple internet connection. It’s a lot like ditching your old DVD collection for a streaming service. You still get the movies (your data and applications), but you don’t have to own the physical discs or the player (the server hardware).
A crucial part of the cloud is the pay-as-you-go model. This is key. You only pay for the exact power, storage, or solution you use – just like your electric bill. Is your business slammed during the holiday rush? The cloud automatically gives you more capacity without you lifting a finger. Things slow down? Those resources shrink back, and so does your bill. This is a massive plus of cloud computing for small business over old methods, where you had to overbuy hardware just to handle your busiest day, leaving it mostly unused the rest of the year.
You use cloud computing daily:
- Google Drive or Dropbox: That’s how you store and share important files online.
- Netflix or Spotify: Streaming multimedia instead of using physical media.
This fundamental shift means small businesses no longer need to spend big money or hire staff just to maintain expensive infrastructure. It frees up your capital and your team’s focus. Now you can concentrate on your core mission: serving customers and growing your organization. Cloud services adapt perfectly to your business size, whether you’re three people or thirty.
Practical uses of cloud computing in business
Cloud technology does more than save you money on equipment; it actively helps your daily operations, makes collaboration better, and boosts overall efficiency. Let’s look at how cloud computing in small business plays out in the real world.
File storage and easy access
Before the cloud, sharing a large design file often meant slow emails or setting up complicated ways to access a local server. What a headache.
Cloud-based file storage (like Google Drive, OneDrive, or Amazon S3 for heavy lifting) has fixed this. It gives you secure remote access to all your files. You can get them from anywhere and on any device. Whether you’re on your laptop at the coffee shop or using a tablet at a client’s office, your files are right there.
Automated backup solutions
Every small business owner dreads data loss. It can happen because a hard drive fails, a fire breaks out, you get hit with ransomware, or maybe an employee just accidentally deletes a critical folder.
Cloud technology offers automated data backup solutions. These quietly work in the background, protecting your business from disaster. Forget swapping out physical backup tapes every night. The cloud automatically encrypts your data and sends copies to secure, off-site data centers.
Scalable cloud hosting
If you run a website, an e-commerce shop, or any custom application, you need hosting. Traditional hosting puts your site on a single, physical server. If your website suddenly goes viral and traffic explodes, that one server can easily crash. Hello, lost revenue and frustrated customers.
Cloud hosting is different. It spreads your website or application across a giant network of virtual servers – the cloud.
Key cloud hosting benefits:
- Automatic scalability: Your capacity instantly adjusts to your traffic. Hit with a huge spike? The cloud spins up more resources. No worries.
- Reliability: If one server in the network goes down, others immediately take over the load. This means better uptime and a smoother experience for your customers.
- Cost savings: You only pay for what you use. This is much more cost-effective than buying a massive dedicated server that only runs at full power a few times a year.
Software as a Service (SaaS) tools
SaaS (Software as a Service) is the easiest and most common way small businesses start their cloud adoption. These are subscription applications you use right from your web browser or a simple phone app.
The best part of SaaS? You never have to worry about buying licenses, installing programs, or running updates. The provider handles everything. This makes your whole IT operation unbelievably simple.
| Business Function | SaaS Tool Example | Benefit for Small Business |
| Accounting | QuickBooks Online | Simple expense tracking, payroll, and invoicing without the messy installation. |
| CRM/Sales | HubSpot or Salesforce | Manage customer leads, monitor your sales process, and automate follow-ups easily. |
| Project Management | Asana or Trello | Keep teams organized, track tasks, and monitor timelines from one clear place. |
| Communication | Slack or Microsoft Teams | Unified chat, video calls, and file sharing for seamless local and remote teams. |
SaaS tools are how small businesses stay productive. They give you instant access to powerful features while drastically cutting down on internal IT costs and administrative headaches.
_______________________________________________________________________
Ready to see real cloud savings?
Don’t fall behind your competitors. Contact IT-Magic for a consultation. We’ll look at your current IT setup and design a personalized cloud migration plan that fits your budget and growth targets.
_______________________________________________________________________
Cloud hosting vs. traditional web hosting: What’s the difference?
When a small business sets up its website or application, a key early decision is hosting. Most owners end up comparing traditional hosting with cloud hosting. Knowing the difference here is vital because one is far more flexible and reliable.
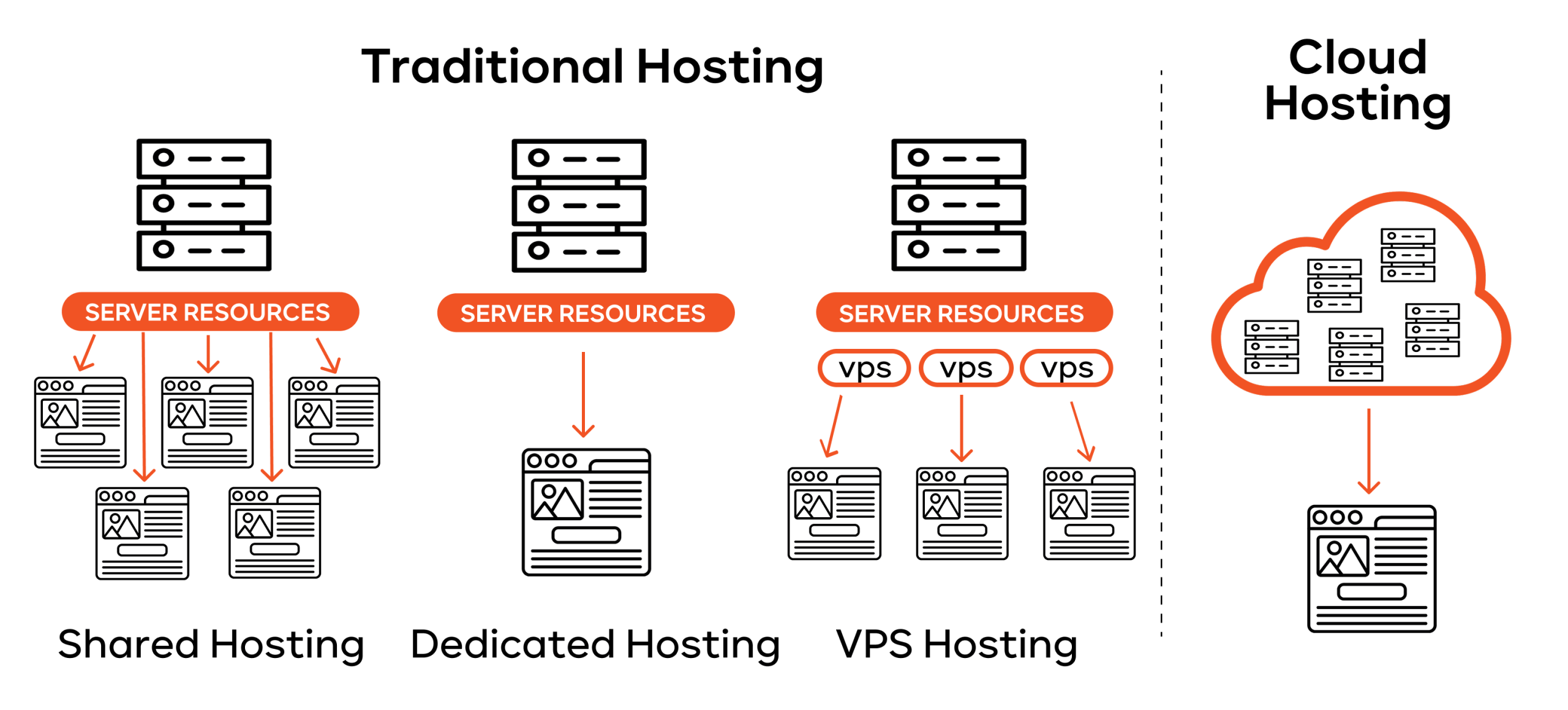
How traditional hosting works
With traditional hosting, your website or application is on one single, physical server. This server is in a provider’s data center. This can be a shared server (your site shares space and risk with hundreds of others), a dedicated server (you rent the whole physical machine), or a virtual private server.
The big drawback is that traditional hosting is totally limited by that one machine’s power.
- No real scalability: If your traffic suddenly explodes, the server will likely get overwhelmed and crash. Fixing this requires adding physical hardware, which takes time and money.
- Hardware failure: If that single server’s hard drive or power supply fails, your entire website is down until someone can physically go and repair it. You get longer, more frequent periods of downtime.
- Fixed costs: You pay for the physical server’s maintenance, power, and cooling, no matter how much you actually use it.
Why cloud hosting offers more flexibility
Cloud hosting uses a method called distributed hosting. Your website’s files and resources are spread out across a network of virtual servers – the cloud.
When a customer visits your site, the content is delivered from the best-performing server in that network. This design offers huge benefits:
- Automatic redundancy: Since the site runs on many servers, if one fails, another immediately steps in to handle the traffic. This virtually eliminates unscheduled downtime and makes your service much more reliable.
- True pay-as-you-use pricing: You start small. If your business traffic jumps, the network instantly gives you the extra power needed. You only pay for the exact resource consumption, making it highly cost-efficient, especially for businesses with unpredictable traffic.
- Performance: Spreading the workload across a huge network means your pages load faster. This is great for customer experience and vital for ranking well on search engines like Google.
For a small business, this extra flexibility and reliability mean you spend less time solving IT crises and more time growing your business.
Cloud service models explained
Cloud computing isn’t just one simple product you buy. Providers offer services in three main categories, often called “as a Service.” These categories define who manages what. Understanding them is critical to choosing the right solution for your needs.
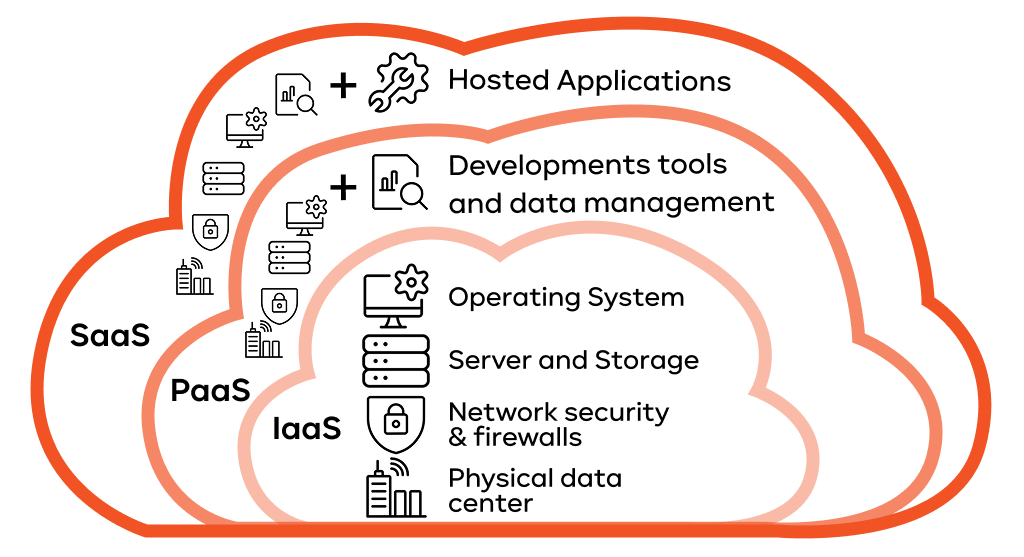
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
Think of it this way: You want to build an office building. You don’t want to buy the land or handle the foundation work. You just want to rent the completed shell, the plumbing, and the electricity. That’s essentially IaaS.
- What it is: IaaS is the most basic cloud offering. You rent the essential computing resources – virtual servers, storage, and networking – from the provider.
- Examples: AWS EC2, Microsoft Azure Virtual Machines, Google Cloud Compute Engine.
- Who uses it: Businesses that need full control over their operating system or want to run custom or older software. You manage the software, but the provider manages all the physical hardware.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
Using the same analogy, you rent the foundation and utilities, but you also get all the major interior components, like pre-built offices, elevators, and a basic HVAC system included. You just worry about moving in your furniture and running your business.
- What it is: PaaS gives you the infrastructure (IaaS) plus a complete, ready-to-use environment. This includes the operating system, database, and web server.
- Examples: AWS Elastic Beanstalk, Google App Engine, Heroku.
- Who uses it: Software developers or companies that want to build, test, and deploy custom applications quickly. They can skip the tedious work of managing servers, which speeds up the development process.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
This model is the simplest one. Think of it like renting a fully furnished apartment. You just move right in and start using it immediately.
- What it is: SaaS is a complete, cloud-based software application. You access it through a browser or an app. The provider handles absolutely everything: hardware, software, security, and updates.
- Examples: Google Workspace (Docs, Gmail), Salesforce (CRM), Zoom, Shopify.
- Who uses it: Practically everyone! SaaS makes IT management simple, gives instant access to powerful business tools, and drastically reduces the need for expensive local IT staff. This is one of the biggest benefits of cloud computing for small business.
To pinpoint the right blend of services for your growth plan, getting professional advice is always smart. Our cloud consulting services can give you the expert assessment you need.
Cloud deployment models and security
In addition to the service models (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS), cloud environments also differ in how they are set up – these are the deployment models. Your choice here depends on your budget, size, and especially your security or regulatory needs.
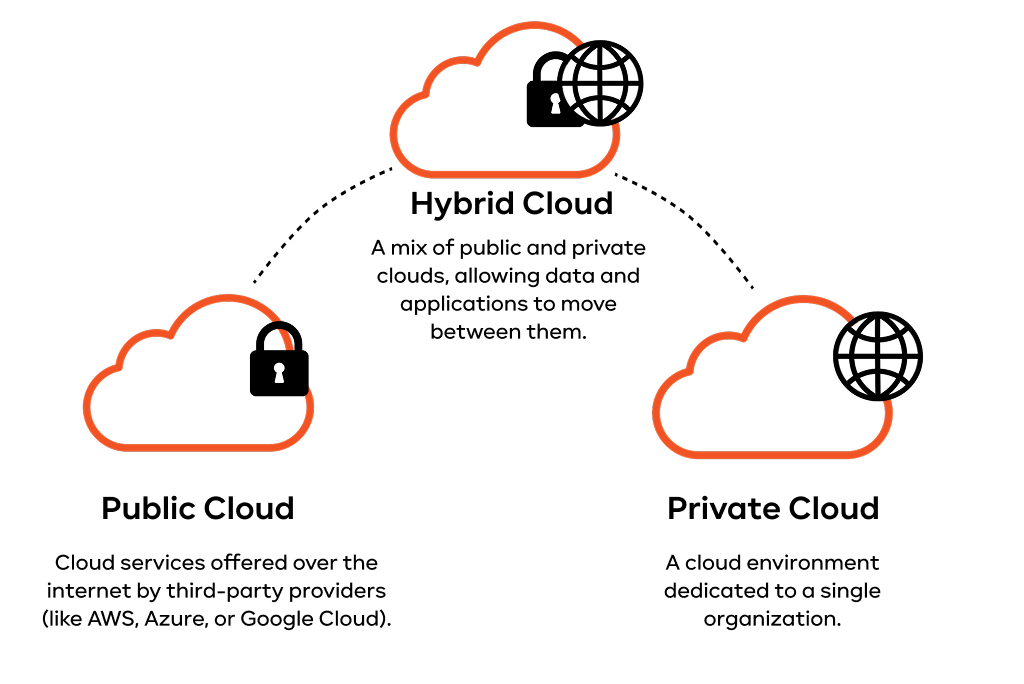
Public cloud: Affordability and scalability
The public cloud is the most widely used and easy-to-access model.
How it works:
Services like AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud are run by a third party. They are shared environments – the provider’s physical hardware is used by many different customers, but your data and applications are kept completely separate and secure using smart virtualization technology.
Benefits:
- Cost savings: You pay for usage, not maintenance. The sheer scale of these providers makes the service incredibly cheap.
- Flexibility: You can scale up or down instantly, without limits.
- Minimal management: The provider handles all the tricky parts: hardware maintenance, security, and updates.
Ideal for: Startups, most small businesses, development work, and any organization needing fast deployment and huge flexibility.
Private cloud: Security and control
A private cloud is dedicated infrastructure used exclusively by one organization. It’s like having your own, custom-built data center.
How it Works:
The servers can be on-site at the company’s facility or hosted by a third party, but the key is that all the resources are reserved just for that single business.
Benefits:
- Total control: Maximum control over security protocols, customization, and exactly where your data is stored.
- Compliance: Makes it much easier to meet strict regulatory needs in specific industries (like HIPAA for patient data).
Ideal for: Heavily regulated industries (finance, healthcare) or large companies with unique security requirements.
Hybrid cloud: Best of both worlds
The hybrid cloud computing model is a smart combination of the public and private clouds. It allows data and applications to move seamlessly between the two.
How it works:
A business might keep its most sensitive financial data in a secure private cloud. However, they would use the affordable public cloud for their customer-facing website or general email system.
Benefits:
- Flexibility and cost: You get the security and control of a private setup for sensitive data, but the cost savings and easy scalability of the public cloud for everything else.
Note: This is becoming a very popular solution for SMBs who want to balance performance, cost, and security perfectly.
Key benefits of cloud computing for small businesses
Cloud computing is truly the great equalizer. It gives small businesses the tools they need to take on much larger competitors without their huge budgets. By adopting this technology, your organization gains immediate, huge advantages.
So, how can cloud computing help small businesses?
Improve team collaboration and productivity
The cloud is essential for modern, flexible teams, especially if you have remote or hybrid employees.
- Real-time collaboration: Tools like Google Docs or Microsoft 365 let multiple team members edit the same file simultaneously. No more confusion over which version is the current one. Work gets done faster, period.
- Unified communication: Multimedia cloud computing for small businesses uses services like Slack or Microsoft Teams. These centralize chat, video calls, and file sharing into one easy platform.
Support sales and marketing growth
Cloud-based tools provide incredible power for finding, managing, and keeping customers.
- CRM power: Services like HubSpot or Salesforce give even the smallest team a comprehensive Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system. They can track every sales lead, monitor the sales process, and manage every customer conversation perfectly.
- Data analytics: Cloud analytics tools can quickly process huge amounts of data from your website and campaigns. Local servers simply can’t handle this efficiently. This allows small businesses to spot trends, target customers better, and significantly increase sales conversions.
Attract and retain new customers
Providing an excellent customer experience is vital for small business survival, and the cloud makes it achievable.
- Better service: Cloud-based customer support tools (Zendesk, Freshdesk) combine all customer questions (from chat, email, and social media) into one spot. This speeds up the whole support process, leading to faster response times and happier customers.
- Scalability to meet demand: If your product goes viral and you see a massive traffic surge, your cloud-hosted e-commerce platform (like Shopify or a custom setup on AWS) will handle all the new transactions without crashing.
Accelerate time-to-market
In business, moving fast is everything. Cloud platforms drastically cut down the time it takes to get an idea or a service out to your customers.
- Faster development: Using PaaS models, your developers can instantly access all the environments they need for building and testing applications. There’s no waiting for physical servers to be ordered, delivered, and configured.
- Automation: Cloud solutions allow for automated testing and deployment. New features or fixes can go live in just hours, not days or weeks. This quick action gives small businesses a significant competitive edge.
Scale operations without high costs
This is often cited as the greatest of the cloud computing benefits for small business growth.
- Eliminate upfront capital expenditure: You stop buying expensive servers and networking gear that will be outdated soon. Instead, you switch to a manageable monthly operating expense (OpEx). You avoid huge upfront capital investments (CapEx).
- Start small, grow big: A brand-new company can start with tiny resources and a low bill. As they get new clients, the cloud infrastructure can be expanded instantly with a simple click. The financial hurdle to expansion is virtually gone.
Foxtrot
Explore CasePlan your next steps with a cloud migration roadmap
Moving your business to the cloud needs to be a well-thought-out, strategic process, not a rash decision. A clear cloud migration roadmap is absolutely essential for a successful small business cloud adoption.
Here is a simple breakdown of the process:
1. Assess needs and inventory
What exactly are you moving? You need a list of all your current hardware, software, and applications. Determine which ones are truly critical, which can be retired, and which need changing for the cloud. This step also involves defining your main goals (like cutting IT costs, enabling permanent remote work, or improving data security).
2. Choose service model(s)
Based on your list, decide on the right blend of IaaS (for custom needs), PaaS (for development), and SaaS (for standard tools). Most small businesses will use a variety of the best cloud computing services for small business.
3. Select a cloud provider and model
Decide whether a public, private, or hybrid cloud computing model is best. For most SMBs, a public cloud like AWS offers the best overall mix of features, security, and scalability.
4. Plan the migration
Create a detailed timeline for the move. Start by moving less critical data and applications first. This “lift and shift” process takes experience to minimize service interruption.
5. Train staff and update processes
The cloud changes how IT is handled. Make sure your employees are trained on new tools (SaaS) and new security rules (like always using MFA and managing access).
6. Monitor and optimize
Once you’re live, you must continuously check usage, performance, and costs. Because of the pay-as-you-go model, you need constant optimization to make sure you’re only paying for the resources you actually need.
Navigating this transition, especially moving large or complex existing systems, really should be done by professionals. While over 70% of companies report cost savings within a year of moving to the cloud, only those with a well-executed plan achieve these results without significant problems.
Your cloud future starts now!
Are you ready to ditch the old servers and tap into the full potential of the cloud for growth? Contact IT-Magic today to get a comprehensive, no-pressure cloud readiness assessment. Let us help you plan your smart move to the cloud.
FAQ
We want to leave you feeling secure, so here are quick answers to common small business concerns.
How much does it cost to implement cloud solutions?
The great thing about cloud computing for small business is the flexibility in pricing. The cost depends on a few things:
- Number of users: Most SaaS tools charge per user, per month.
- Storage and data transfer: You pay based on the volume of data stored and the amount of data transferred out of the cloud.
- Complexity: Customized IaaS or PaaS setups for unique applications will have higher costs based on the specific virtual resources they consume.
While you pay a monthly fee, the total cost is nearly always lower than the total cost of ownership (TCO). TCO includes buying and maintaining physical servers, paying IT salaries, and the huge hidden costs of downtime and data loss. The cloud changes a massive capital expense into a simple, predictable monthly operating expense.
Is cloud computing safe for small businesses?
Yes, absolutely. When set up correctly, cloud computing is typically much safer than relying on the security a small business can manage on its own. Top providers like AWS and Azure spend billions on their security infrastructure.
- Key security features: They use military-grade data encryption. They have sophisticated access control systems. They maintain strict, global compliance certifications (like ISO 27001, SOC 2, and GDPR).
- Small business responsibility: Security is a shared job. The provider secures the cloud infrastructure, but you secure your data within the cloud. This means always enabling Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) on all accounts, using strong passwords, and carefully managing file permissions.
What risks should small businesses consider before adopting cloud services?
The advantages of cloud computing for small business are huge, but no technology is perfect. It’s smart to know the potential risks before you commit.
- Data Privacy and Location: Be sure you know where your data is stored. Check that the provider’s rules comply with any specific regulatory needs for your industry.
- Downtime (service outages): While rare, outages can happen. Review the provider’s Service Level Agreement (SLA) to see their uptime guarantees and how they compensate for service interruptions.
- Vendor lock-in: Moving from one cloud provider to another can be complicated and costly. Choose a provider with good data export tools. Make sure your data can be easily retrieved if you ever need to leave.
- Cost overruns: The pay-as-you-go model, while a benefit, requires ongoing monitoring. If a service is accidentally left running or is poorly configured, costs can climb quickly.
How to fix it: Only choose trusted providers. Use cloud backup solutions that are separate from your main service. Most importantly, work with an experienced consultant to design and monitor your cloud platform from day one.




