Ever feel like your apps aren’t talking to each other? A customer signs up, but your welcome email never sends. A server fails, but your support team is the last to know. It’s a common problem. Your various software tools work in their own little bubbles. What you really need is a go-between, a central hub that lets all your services share information instantly.
This is where AWS EventBridge comes in. Think of it as the traffic controller for your cloud setup. This guide will answer the question “What is EventBridge?”, how it works, and why it’s a must-have for building modern apps. It’s a powerful service that helps you create an event-driven system. This means your applications can react to things as they happen, making your whole business run smoother.
This guide will break down what Amazon EventBridge is, how it works, and why it’s a must-have for building modern apps.
Introduction to event-driven architecture
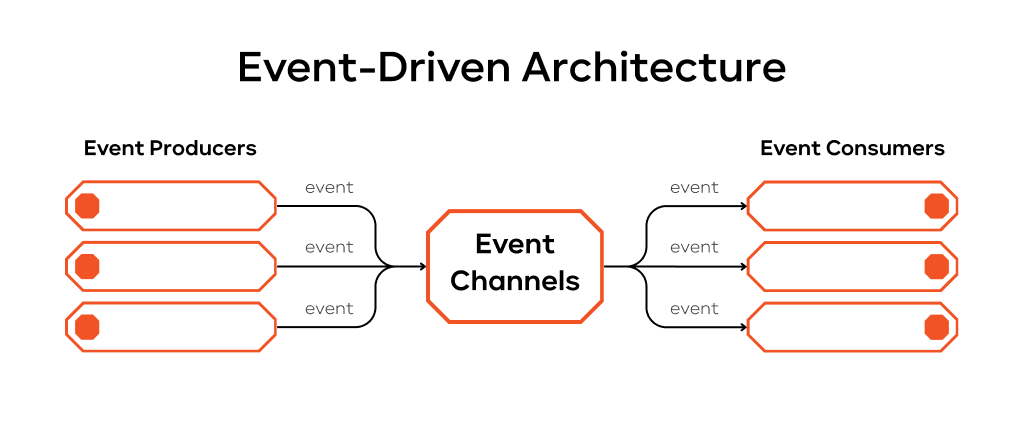
First, let’s talk about the big idea behind EventBridge: event-driven architecture (EDA). Don’t let the fancy name scare you. It’s just a way of building software where different parts communicate through messages called “events.” Instead of one app directly asking another for information, it sends out a broadcast – an event – when something important happens. These events are observable by other apps that can react correspondingly.
An “event” is just a small package of data that signals something happened. It could be almost anything:
- A user creates an account.
- Someone adds an item to their shopping cart.
- A payment goes through.
- Inventory for a product is running low.
- An error occurs on one of your servers.
The event contains facts about what happened. It doesn’t tell any other service what to do. This is the key. The part of your system that creates the event (the “producer”) isn’t tied to the parts that act on it (the “consumers”).
Why is this setup so useful? Here’s the deal:
- Apps don’t need to be glued together: With EDA, your services are independent. Your order service can send an “Order Placed” event. It doesn’t need to know if a shipping app, an email app, or an analytics tool is listening. This “loose coupling” lets you update or add new services without breaking everything else.
- React in real-time: EDA is built for speed. Events are sent and processed the moment they happen. This allows your business to respond instantly to new opportunities or problems.
- Grow without the pain: Because services are separate, you can scale them one by one. If you get a huge spike in orders, you can give your order processing service more power without touching anything else. Plus, if one part of your system fails, it doesn’t crash the whole thing.
You can find EDA running behind the scenes in many places:
- Microservices: They provide an ideal structure for independent services to collaborate effectively.
- IoT (Internet of Things): Think of connected smart devices sharing information with each other. EDA helps you manage and act on this huge flow of data in real-time.
- E-commerce: From placing an order to sending shipping updates, EDA powers the entire journey.
Overview of AWS EventBridge
So, what is AWS EventBridge? It’s a serverless tool that acts as a central post office for all your events. It gathers events from various sources, looks at who they are for, and sends them to the right place based on rules you set.
Within the AWS world, Amazon EventBridge is the heart of your event-driven architecture. It easily connects your own apps, third-party SaaS tools, and other AWS services. This lets you build smart workflows that connect everything. For example, you could say, “When a new lead is added in Salesforce, trigger a function in AWS to add them to our email list.”
If you’ve used AWS for a while, you might know CloudWatch Events. AWS EventBridge is the newer, more powerful version. It uses the same reliable technology, so your old CloudWatch Events rules still work. But EventBridge adds a huge new feature: direct integrations with SaaS partners. This makes it much more useful for connecting your entire business.
EventBridge can receive events from many places:
- Over 200 AWS services: Almost every AWS service (like S3, EC2, and Lambda) produces events that EventBridge can listen to.
- Your own apps: They can send their events to EventBridge with minimal setup using a simple command.
- SaaS applications: This is a huge plus. EventBridge connects with over 500 tools you already use, like Zendesk, Shopify, and Datadog. This lets you automate tasks based on what happens in those platforms.
EventBridge AWS is “serverless.” This gives you two big wins:
- No servers to manage: You don’t have to worry about setting up, patching, or managing any servers. AWS handles it all for you.
- Grows with you: EventBridge scales up or down automatically based on how many events you have. It operates reliably, whether the event volume is low or very high.
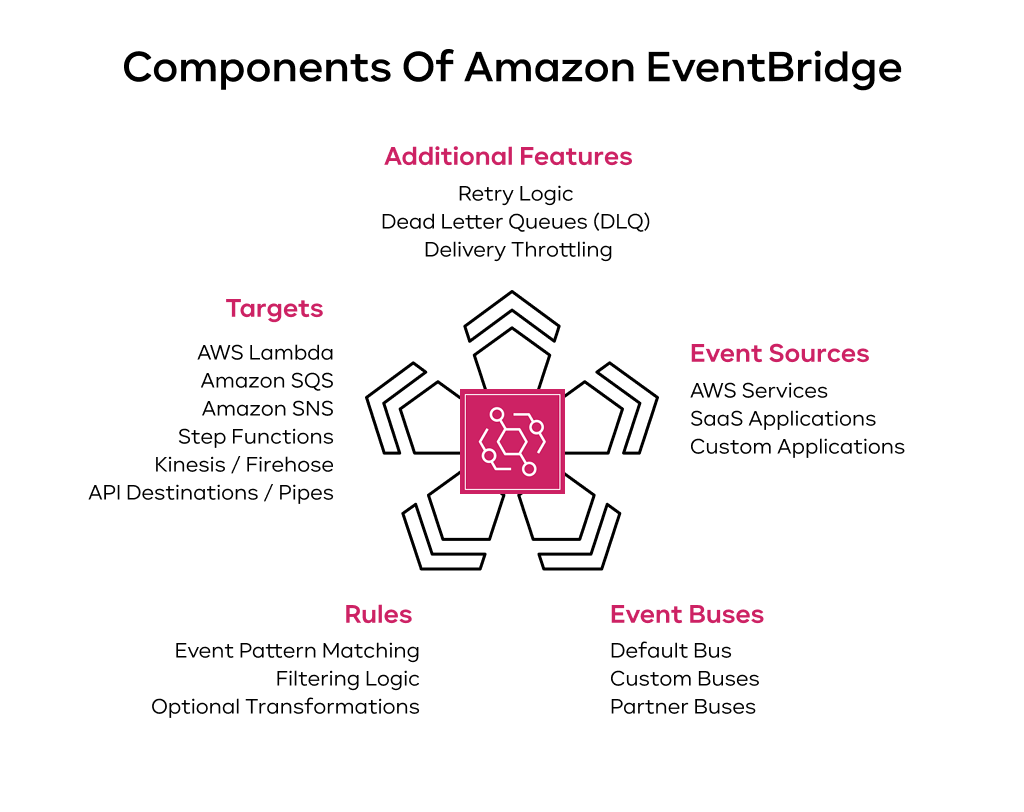
Core components of EventBridge
To really get the hang of AWS EventBridge, you need to know its main parts. They collaborate to detect, classify, and deliver your events.
Event definitions
Events in Amazon EventBridge are just simple JSON text objects. The content changes depending on the source, but they all have a similar wrapper.
Every event has a standard structure with a few key fields:
- source: Which service or app sent the event (e.g., aws.s3).
- detail-type: A short description of the event (e.g., “Order Created”).
- detail: The event’s main payload. This is a JSON object with the specific info about what happened.
- time: A timestamp for when the event occurred.
Events from AWS services have a set structure. For example, an event for a new file in S3 will always include the file name and bucket name. When you send your own custom events, you get to decide what goes in the source, detail-type, and detail fields. This lets you create event structures that fit your app perfectly.
An event source is anything that creates an event. AWS EventBridge works with a few types:
- AWS services: Services like Lambda and EC2 are integrated with EventBridge as built-in event sources.
- Custom applications: Any app you build can be an event source. Events can be sent by executing the PutEvents command.
- SaaS applications: You can set up tools like Shopify or Zendesk to send events right into your AWS account. This is done through “Partner Event Sources.”
Event buses explained
An event bus is the main channel where events travel. Think of it as a central highway for all your event traffic.
You get three kinds of event buses:
- Default Event Bus: Every AWS account comes with a default bus. It automatically gets events from other AWS services.
- Custom Event Buses: You can create your own buses for your custom apps. This is a great way to keep different projects separate and organized.
- Partner Event Buses: These buses are specifically for receiving events from your SaaS partners.
The event bus is where everything starts. All events, no matter where they come from, are sent to a bus. The bus then checks the event against your list of rules to see where it should go next.
Event rules and filtering
Rules are the brain of EventBridge. A rule looks for certain events and sends them to a target for processing.
Each rule has an “event pattern.” When an event arrives, AWS EventBridge checks its pattern. If the event is a match, EventBridge sends it to the target listed in that rule.
Event patterns are also JSON objects. They act like a filter. Filtering can be applied to any field within the event. For example, you can create a rule that only catches events from the aws.ec2 source that are about a server shutting down.
Good filtering saves you time and money. By writing very specific rules, you make sure your other services (like a Lambda function) only run when they truly need to. It ensures that resources are used efficiently by ignoring irrelevant events.
Event targets
A target is the final destination. It’s the service that EventBridge sends the event to after it matches a rule.
EventBridge can send events to a long list of AWS services, including:
- AWS Lambda functions
- AWS Step Functions workflows
- Amazon SNS topics and SQS queues
- Amazon Kinesis data streams
- API Gateway
- And EventBridge Pipes for direct, one-to-one connections
One rule can direct an event to multiple targets. For instance, when a new order comes in, one rule could trigger three things at once: a Lambda function to process the payment, an SNS topic to notify the warehouse, and an archive to save the order information.
AWS EventBridge is built to be reliable. It will continue sending the event for up to 24 hours if the target is busy or offline. If it still can’t get through, you can set up a dead-letter queue (DLQ). This is a safe place to store failed events so you can look at them later.
_______________________________________________________________________
Confused, trying to figure out the best way to set up a reliable and scalable event-driven system?
If you need a hand designing your event flows, writing rules, or picking the right targets, our experts at IT-Magic are here to help.
_______________________________________________________________________
Ideal scenarios for using AWS EventBridge
So, when is AWS EventBridge the right tool for the job? It’s a great fit anytime you need to connect different systems in real-time. Here are a few perfect scenarios:
- Real-time application workflows:
Think about an online store. A customer confirms an order, and an event is created. EventBridge sends this event to the shipping service, the email notification service, and the inventory service all at the same time.
- Decoupled microservices communication:
In a microservices architecture, different services need to share information without being directly tied together. EventBridge acts as the middleman. A “user service” can announce a UserSignedUp event, and other services like “billing” or “analytics” can listen and react without the user service even knowing they exist.
- Integrating third-party SaaS with AWS services:
This is where AWS EventBridge is a superstar. You can start workflows in AWS based on actions in other platforms. For example, a new ticket in Zendesk could trigger a Lambda function to pull up customer history from your database and add it as a private note to the ticket.
- Serverless workflow orchestration:
You can use EventBridge to create a chain reaction of serverless functions. Consider a scenario where a user uploads an image to Amazon S3. This triggers a Lambda function to resize it. When it’s done, that function sends an ImageResized event. EventBridge then sends this event to another function that adds the image details to a database.
- Data ingestion pipelines:
For IoT devices or application logs, you can have them all send event data to EventBridge. From there, you can route it anywhere you need for processing, like Amazon Kinesis for live analytics or Amazon S3 for storage.
Key advantages of AWS EventBridge
Choosing AWS EventBridge gives you some major wins. It helps you build faster, more reliable systems that cost less to run. Let’s look at the top benefits.
Loosely coupled system architecture
One of the core strengths of EventBridge is its ability to design a loosely coupled system. In older systems, components were often directly connected. If you changed one part, you risked breaking another. Amazon EventBridge avoids this. Services talk through the event bus, not directly with each other. This means your teams can work on various services at the same time. You can update, replace, or scale one service without causing a domino effect.
High scalability and adaptability
EventBridge is a fully managed, serverless service. This means it grows with you automatically. You never have to think about adding more servers or managing capacity. It adapts on the fly, whether you have a slow trickle of events or a massive flood. This allows your architecture to manage high-traffic periods automatically.
Support for real-time data processing
EventBridge is built for speed. It can take in and process events with very little delay. It delivers event data from a source to a target like AWS Lambda almost instantly. This is vital for jobs that need immediate action, like stopping fraud, tracking live sales data, or creating a snappy user experience.
Easy integration across services
Connecting different systems is what Amazon EventBridge does best. It’s the glue for your entire tech stack.
EventBridge works out of the box with over 200 AWS services. This makes it incredibly easy to create automated workflows that span the entire AWS ecosystem.
Its ability to connect with over 500 SaaS tools like Salesforce is a game-changer. You can set up event sources from these platforms in a few clicks. This lets you react to important business events no matter where they happen.
Cost-efficient operations
The way EventBridge is priced makes it very friendly for your budget.
With AWS EventBridge, you only pay for the events you publish. There are no monthly minimums or startup fees. Events from AWS services are free. You can start affordably and avoid paying when there’s no activity.
Since it’s serverless, you don’t have to worry about infrastructure management. You save all the time and money you would have spent on patching, monitoring, and scaling servers. As a result, your team can concentrate on features that provide value to your customers.
Highlighted AWS EventBridge capabilities
Beyond the basics, AWS EventBridge has some special features that let you build very smart and efficient systems. These tools offer enhanced control and easy automation of complex tasks without heavy coding.
Smart event routing and rule-based logic
The real magic of EventBridge is in its smart routing. You can create very detailed rules that filter events based on what’s inside them. This lets you route events with pinpoint accuracy. You can send different event types to different targets, or send one event to many places at once for parallel processing.
Built-in integration with AWS and 500+ SaaS tools
We’ve said it before, but it’s a big deal. The massive library of built-in connectors for SaaS apps saves a ton of time. Instead of writing custom code and managing security tokens for webhooks, you just configure a partner event source. This helps you build automations that connect all your tools in record time.
EventBridge Pipes for low-latency stream processing
AWS EventBridge Pipes is a feature that makes one-to-one integrations simple.
A Pipe is like a dedicated, direct pipeline from one source to one target. It’s perfect for when you need to take events from a source like an Amazon SQS queue or a Kinesis stream and send them reliably to a target like a Lambda function.
Pipes also let you filter, change, and add to events while they’re in transit. This means you can weed out events you don’t need, change the event’s format, or even add extra data from another service before the event gets to its destination. This cuts down on the amount of code you have to write in your target services.
EventBridge Scheduler for serverless task automation
The EventBridge Scheduler is a smart timing tool for running your cloud jobs.
This feature lets you create millions of schedules to trigger over 270 different AWS services. You can set up schedules that run just once or set them to repeat using familiar cron or rate formats.
With the Scheduler, you no longer need to run cron jobs on servers or pay for an external scheduling service. It’s a fully managed, serverless tool that’s more reliable and easier to use. It’s great for things like running daily reports, doing regular maintenance, or starting workflows at a specific time.
Event archiving and replay options
EventBridge also has features for saving and re-sending events. This is a lifesaver for fixing bugs, meeting compliance rules, and recovering from errors.
You can create an archive for any event bus. It will save all the events that pass through it for a period of time you define. If one of your services goes down or you find a bug, you can use the “replay” feature to resend those archived events once you’ve fixed the problem. This ensures you don’t lose any data.
Notable Amazon EventBridge functionalities
Let’s zoom in on some of the specific functions that make Amazon EventBridge so useful for developers.
Fine-grained event rule filtering
AWS EventBridge rules can be incredibly specific. You can filter based on data deep inside the event message, match parts of a word, or check if a field even exists. This level of control makes sure your targets only wake up for the exact events they care about.
Content-based routing mechanisms
This powerful filtering lets you route events based on their content. For example, an order.created event could normally go to a “Standard Shipping” workflow. But if the event contains a field like priority: “express”, a different rule can grab it and send it to an “Express Shipping” workflow instead.
Support for Schema Registry
The EventBridge Schema Registry helps you keep track of your event structures.
- It discovers and saves the “schema,” or blueprint, of events on your event bus.
- It helps you write code faster. You can download code templates based on these schemas for languages like Python or Java. This lets you work with clean, predictable event objects in your code.
- It acts as documentation. The registry makes it easy for all your developers to understand what data to expect in various events.
Transforming event messages
You can change an event’s message before it reaches its target. The “Input Transformer” lets you customize the JSON text the target receives. You can pull out certain values, add new information, or completely change the structure to match what the target expects.
Custom event creation
Your apps can be producers, not just consumers. Using the PutEvents command, your developers can create and send their own custom events. This lets you plug any part of your custom infrastructure into your event-driven system.
Archival and replay of historical events
Being able to archive and replay events is key to building a strong system. You can use it to debug past problems, test new features with real data, or recover from a system failure without losing data.
Integration with SaaS applications
The simple, built-in connection to hundreds of SaaS partners is a huge time-saver. Connecting your AWS environment to tools like Salesforce or Datadog becomes a quick configuration task, not a long coding project.
Sending events to API Destinations
With API Destinations, you can send events to any web address. This lets EventBridge trigger systems outside of AWS, like a legacy app or any third-party service with an API.
Scheduled event triggers
The EventBridge Scheduler lets you create time-based triggers. You can run them on a schedule, like every hour, or use cron expressions for more complex timing. It’s perfect for automating all kinds of routine jobs.
Wide range of native sources and destinations
EventBridge connects to a huge number of AWS services. Sources like S3, EC2, and Lambda can produce events, and targets like SNS, SQS, and Step Functions can receive them. This makes it the perfect hub for managing workflows across all of AWS.
Guaranteed and reliable event delivery
Amazon EventBridge is built to be tough. It guarantees at-least-once delivery, so you can trust your events will arrive. With automatic retries and dead-letter queues, it gives you a solid foundation for building reliable apps.
Examples of AWS EventBridge use cases
Let’s look at a few more examples to see how it all comes together.
E-commerce
A customer buys a product. An OrderConfirmed event is created. EventBridge sends this single event to three places at once:
- An AWS Step Functions workflow starts the shipping process.
- An AWS Lambda function sends a thank-you email to the customer.
- The event is also sent to a Kinesis data stream to show up on the live sales dashboard.
Security
You can set up rules to react instantly to possible threats.
- If someone creates a new admin user in your AWS account, an event can trigger an immediate alert to your security team’s phones via PagerDuty.
- If a firewall rule is changed to be less secure, an event can trigger a function that automatically changes it back and flags it for review.
Internet of Things
A smart factory has sensors on all its machines.
- A sensor detects that a machine is overheating and sends a HighTemp event.
- EventBridge routes this to a Lambda function that creates a maintenance ticket.
- If several sensors in one area send alerts, a different rule could trigger a full shutdown of that production line to prevent a major failure.
SaaS integrations
A company uses Salesforce for sales.
- A salesperson closes a deal and marks the lead as “Won.” This action in Salesforce sends an event to EventBridge.
- This one event kicks off a whole process: a Lambda function creates a new account for the customer in the main app, another function adds them to the billing system, and a third sends them a welcome email.
Summing things up
As you can see, AWS EventBridge is a flexible and powerful tool that can be the backbone of any modern application. It helps you build more scalable and resilient systems by letting your services communicate in real-time. By connecting everything from your own applications to AWS services and the SaaS tools you use every day, EventBridge helps you automate more and innovate faster.
If you’re excited about building a more responsive business with event-driven architecture but want some help getting started, we’re here for you. The team at IT-Magic has deep experience designing and building powerful solutions with AWS EventBridge.
Ready to build a smarter and more automated business?
Unlock the full power of AWS EventBridge with the help of our team. Get in touch for a free consultation.
FAQ
When should I choose EventBridge?
Choose AWS EventBridge when you need a smart router. Use it for complex routing based on the event’s content, especially when you need to connect SaaS apps with AWS services. Think of it as a smart mail sorting facility.
Can EventBridge handle real-time data streams?
Yes, Amazon EventBridge works in near real-time. It’s great for starting real-time workflows. For super low-latency connections, EventBridge Pipes is a fantastic feature. It can pull records from a stream like Kinesis and send them directly to a target with very little delay.
Can I schedule tasks using AWS EventBridge?
Yes, absolutely. The EventBridge Scheduler lets you create time-based rules. You can run tasks every X minutes or on a complex schedule with cron. This lets you automate just about anything without managing your own scheduling servers.